guess you like
BHX Combined-Flow Closed-Circuit Cooling Tower – Scalable, Efficient, and Low-Scaling Design
BNX Counterflow Closed Circuit Cooling Tower – High-Efficiency Industrial Heat Exchanger
ZNX Counterflow Evaporative Condenser – Compact, High-Performance Heat Rejection
ZHX Combined Flow Evaporative Condenser – Enhanced Efficiency with Fill-Assisted Heat Transfer
Cooling Coil
Drift Eliminator
PVC Fill
Fan
Spray Nozzle
V-type Air Cooler
ZNX Counterflow Evaporative Condenser
Product Overview
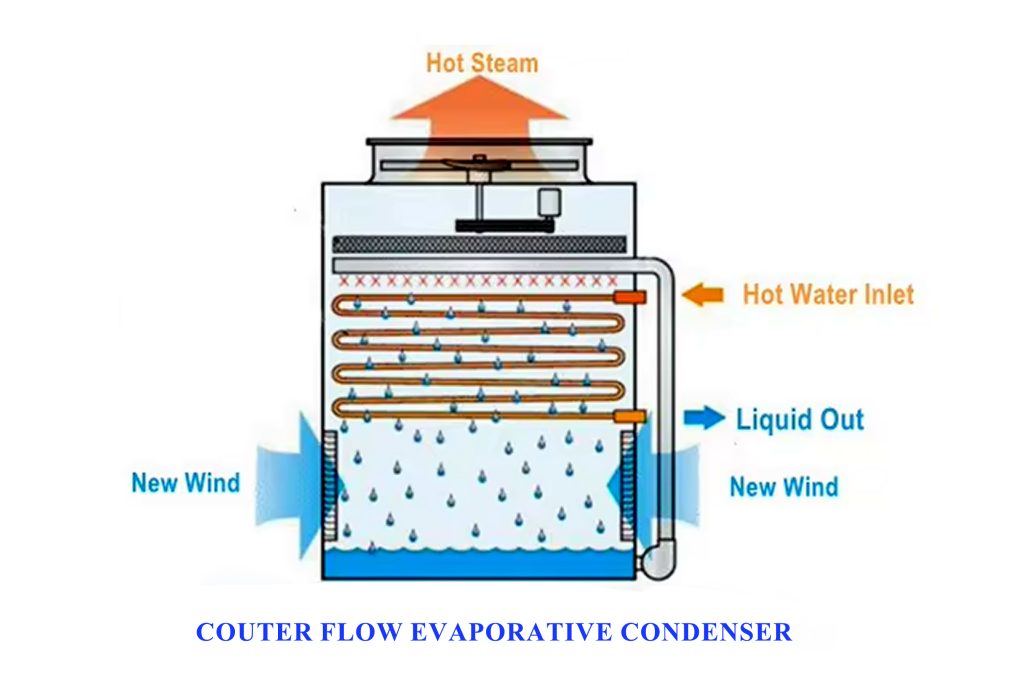
The ZNX Counterflow Evaporative Condenser integrates condensation and heat rejection in a single piece of equipment. Refrigerant vapor condenses inside the closed coil while water is sprayed over the coil surface and ambient air is drawn upward by axial fans in a counterflow pattern (air bottom→top, water top→bottom). This geometry maximizes the log-mean temperature difference (LMTD), reduces footprint, and achieves a low condensing temperature for substantial compressor power savings compared with dry coolers or air-cooled condensers.
Working Principle
Hot refrigerant vapor enters the top of the coil bundle and condenses as recirculated water is uniformly sprayed over the coil surface, forming a thin cooling film. Axial fans draw air upward from the louvered bottom intakes to the fan deck, enabling both sensible heat transfer (coil to water/air) and latent cooling as a small portion of the spray water evaporates.
The warmed air and vapor are exhausted by the fans, while drift eliminators capture droplets and return the collected water to the basin for recirculation. With no internal fill, the ZNX condenser offers greater space for enlarged coil surface area, delivering higher heat rejection capacity within a compact footprint and reduced installation space requirements.

Refrigerants & Thermodynamics
ZNX supports ammonia (NH3), CO2, and low-GWP HFO/HFC blends. Evaporative heat rejection allows the condensing temperature to run only a few Kelvin above the ambient wet-bulb temperature (typically 3–6 K approach), trimming compressor lift. On a pressure–enthalpy (p–h) diagram, a lower condensing pressure reduces compression ratio and specific work, improving system COP. For transcritical CO2, ZNX can be applied in subcritical cascade or parallel compression systems where the condenser operates below critical conditions.
Applications
- Cold Storage & Food Processing: Low and medium temperature ammonia refrigeration.
- Beverage & Brewery: Stable condensing for seasonal loads.
- Pharma & Chemical: Reliable heat rejection with clean closed coils.
- Ice Plants & Rinks: Low approach enhances compressor efficiency.
Advantages
- No infll designed, more compact structure, lower profle, less installation area required, and easy for transport andinstallation.
- Suitable to severe environment as its structure muchmore close, which could prevent from sand and dust.
- Suitable to high temperature fuid, because hot spraying water will not distort pVC fill as no pVC fill designed.
- Freezing resistance,because there is no PVC fill to slow down spraying water flow speed.
Sizing & Selection
Key inputs include heat of rejection (kW), design wet-bulb (°C), desired condensing temperature (°C), water quality, and site constraints. Counterflow favors the smallest footprint. Typical water flow is selected to ensure full coil wetting while limiting pump head. For noise-sensitive sites, choose larger diameter low-speed fans with VFD. For aggressive atmospheres or corrosive water, specify stainless steel coils (SS304/316) and heavy-duty casing finishes.
Energy & Water Efficiency
Compared with air-cooled systems, ZNX cuts compressor power by lowering condensing temperature. Water consumption consists of evaporation (proportional to load), drift (minimized by eliminators, ≤0.001%), and blowdown (to control cycles of concentration). Using conductivity-based blowdown control, side-stream filtration, and high-efficiency nozzles balances water use and cleanliness. Optional adiabatic pre-filters can reduce fan power during peak heat.
Materials & Anti-Corrosion
Standard coils are hot-dip galvanized with optional epoxy or stainless steel for harsh duty. Casing panels are galvanized or pre-painted steel; SS options available. Polymeric drift eliminators and PVC/PP wetted parts resist scaling and UV. Basin protection includes sacrificial anodes or coatings when required.
Controls & Options
- PLC/BCU with condensing pressure setpoint control.
- VFD fans with temperature/pressure resets; pump staging.
- Winterization: basin heaters, variable spray, dry operation assist.
- Maintenance: hinged access doors, clean-out drains, quick-change nozzles.
Installation & Maintenance
Provide straight air intake, structural support with vibration isolation, and clean water supply with filtration. Commission with coil pressure test, verify spray coverage, set fan rotation, and calibrate level controls. Routine tasks include nozzle inspection, basin cleaning, bleed calibration, and seasonal lay-up.
Development Trends
Trends include lower-GWP refrigerants, ultra-low drift designs, hybrid adiabatic coils, and digital twins for predictive maintenance. Materials innovation (duplex SS, advanced coatings) further extends lifecycle in corrosive environments.



